(Rev.1 Rel.10 March 2012)
Photos and Brief History of the highly successful
Cessna T-37 Trainer and A-37 Attack Aircraft
Story © 2012 by Tom Hildreth
Photos by Tom Hildreth and attributed photographers
If you would like to contribute information
and/or photos,please SEND EMAIL
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Air Training Command (ATC) T-37 Organizations, 1974 7
|
||
| Squadron | Wing | Base |
| 559 FTS | 12 FTW | Randolph AFB, TX |
| 37 FTS | 14 FTW | Columbus AFB, MS |
| 43 FTS | 29 FTW | Craig AFB, AL |
| ? FTS | 38 FTW | Moody AFB, GA |
| 85 FTS | 47 FTW | Laughlin AFB, TX |
| 35 FTS | 64 FTW | Reese AFB, TX |
| 8 FTS | 71 FTW | Vance AFB, OK |
| 82 FTS | 78 FTW | Webb AFB, TX |
| 89 FTS | 80 FTW | Sheppard AFB, TX (NATO) |
| 96 FTS | 82 FTW | Williams AFB, AZ |
| 454 FTS | 323 FTW | Mather AFB, CA |
| Prior to 1972, a four-digit ATC wing designation system existed. The new T-37A/Bs were delivered to those earlier organizations. At the time, the T-37 operated in natural metal finish. | ||
A-37 in Brief
By the late 1940s, the Air Force fielded several first line jet fighter aircraft such as the Lockheed F-80 Shooting Star, Republic F-84 Thunderjet and North American F-86 Sabrejet. In 1950, when faced with a deteriorating situation in Korea, the young service found itself without a suitable close air support (CAS) aircraft. What was needed was an aircraft capable of operating from the smaller Korean airfield, with a suitable loiter time, and capable of defending its home base if necessary. Only by drawing together the F-51 Mustangs that remained in theatre, and by quickly stripping Air National Guard units of their F-51s and shipping them over in large numbers was the Air Force able to successfully fulfill that need.9
A dozen years later, in Vietnam, the Air Force found itself with an impressive array of sophisticated supersonic jet fighters, but was once again without a suitable aircraft for the ground support role. Forced to look afield for suitable airframes, the Air Force quickly and successfully adopted the Douglas A-1 Skyraider, a heavy single-engine propeller aircraft first ordered by the Navy on 6 July 1944.11 There was only a limited number of these old aircraft available, and many Skyraiders were provided to the Vietnam Air Force (VNAF). A new aircraft was urgently needed to equip the U.S. Air Force and that of its ally, the VNAF.
Preceding the CAS deficiencies in the field, two armed T-37Bs (62-5950 and 62-5951) were evaluated at the USAF Special Air Warfare Center during 1962. As development continued, the gross weight of these aircraft increased to 8,700 lb., and an appropriate power increase was made available through the installation of two General Electric J85-GE-5 turbojets. These two aircraft were designated as YAT-37Ds and further weight increase to 14,000 lb. followed. The first flight of aYAT-37D took place on 22 October 1963, and the designation was changed to YA-37A.6
In 1966, the Air Force, under letter contract from Air Force Systems Command requested Cessna to complete 39 T-37Bs then in production as A-37A (Cessna Model 318D) for ground support.
 These aircraft had eight under wing hard points and a 7.62-mm. GAU-28/A Minigun in the right nose section, wingtip fuel tanks, and derated J85-GE-17 engines of 2,400 lb. ST. Delivery of the A-37A began on 2 May 1967, and a 25 aircraft squadron was sent to Vietnam for a computerized evaluation period. The A-37A was judged highly effective in six mission types: Close Air Support (CAS); armed escort of Army troop-carrying helicopters; Combat Air Patrol (CAP) for truck convoys; armed reconnaissance; Forward Air Control (FAC); and night interdiction. Following the evaluation period, the type remained in service with the 604th Air Commando Squadron at Bien Hoa Air Base, and by early 1968 had completed 10,000 combat sorties.3, 6
These aircraft had eight under wing hard points and a 7.62-mm. GAU-28/A Minigun in the right nose section, wingtip fuel tanks, and derated J85-GE-17 engines of 2,400 lb. ST. Delivery of the A-37A began on 2 May 1967, and a 25 aircraft squadron was sent to Vietnam for a computerized evaluation period. The A-37A was judged highly effective in six mission types: Close Air Support (CAS); armed escort of Army troop-carrying helicopters; Combat Air Patrol (CAP) for truck convoys; armed reconnaissance; Forward Air Control (FAC); and night interdiction. Following the evaluation period, the type remained in service with the 604th Air Commando Squadron at Bien Hoa Air Base, and by early 1968 had completed 10,000 combat sorties.3, 6
Construction of the prototype A-37B (Cessna model 318E) began in February, 1967. This variant would be
 able to accommodate the J85-GE-17A engine of 2,850 lb. ST., and would attain a max level speed of 507 MPH, max cruise speed of 489 MPH, and a rate of climb of just under 7,000 Feet per minutes (FPM). The service ceiling was 41,765 ft., with both engines, and 25,000 ft., with one engine operating.3 An in-flight refueling probe was installed on the nose, and the airframe stressed for 6g.6 Production of the A-37B totaled 577 machines, with 164 going to the RVNAF. Delivery to Air National Guard (ANG) units began in 1970, and Air Force Reserve (AFRES) units would equip with the type soon afterward.5
able to accommodate the J85-GE-17A engine of 2,850 lb. ST., and would attain a max level speed of 507 MPH, max cruise speed of 489 MPH, and a rate of climb of just under 7,000 Feet per minutes (FPM). The service ceiling was 41,765 ft., with both engines, and 25,000 ft., with one engine operating.3 An in-flight refueling probe was installed on the nose, and the airframe stressed for 6g.6 Production of the A-37B totaled 577 machines, with 164 going to the RVNAF. Delivery to Air National Guard (ANG) units began in 1970, and Air Force Reserve (AFRES) units would equip with the type soon afterward.5
|
Air National Guard A/OA-37B Organizations |
||
| Squadron | Wing | Base |
| 104 TFS | 175 TFG MD ANG | Baltimore, MD |
| 103 TASS | 111 TASG | NAS Willow Grove, PA |
| 138 TFS | 174 TFW NY ANG | Syracuse, NY |
| 169 TASS | 182 TASG IL ANG | Peoria, IL |
| 172 TASS | 110 TASG MI ANG | Battle Creek, MI |
| 176 TFS | 128 TFW WI ANG | Madison, WI |
|
Air Force Reserve A/OA-37B Organizations |
||
| Squadron | Wing | Base |
| 45 TFS | 434 TFW | Grissom AFB, IN |
| 46 TFS | 434 TFW | Grissom AFB, IN |
| 47 TFS | 917 TFG | Barksdale AFB, LA |
| 706 TFS | 926 TFG | NAS New Orleans, LA |
| 757 TFS | 910 TFG | Youngstown, OH |
Active Duty Air Force A/OA-37B Organizations: As of this writing the author has been no attempt to account in tabular form for the various active-duty organizations that operated the A-37A and A/OA-37B. The author welcomes input from contributors knowledgeable in this area.
Bibliography
1. Jane’s All the World’s Aircraft 1953-1954, pp.210.
2. Jane’s All the World’s Aircraft 1957-1958, pp.263.
3. Jane’s All the World’s Aircraft 1973-1974, pp.303.
4. McGegor, A.J. and Wellen, D., United States Air Force and Army Serial Batches since 1946. Mach III Plus, pp. 18, 1998.
5. Taylor, John, W.R. & Swanborough, Gordon, Military Aircraft of the World, Charles Scribner’s Sons, pp.30, 1973.
6. Swanborough, Gordon, Bowers, Peter M., United States Military Aircraft. Putnam, pp.164, 1989.
7. Pocock, Chris and Smith, Colin, The USAF Today. West London Aviation Group, pp.21, 1975.
8. Jane’s All the World’s Aircraft 1950-1951, pp.268.
9. Futrell, Robert F. The United States Air Force in Korea 1950-1953. Duell, Sloan and Pearce, pp.66, 1961.
10. Wikipedia, Cessna T-37 Tweet.
11. Swanbourough, Gordon and Bowers, Peter M. United States Navy Aircraft Since 1911, 2d Ed., pp.176, 1976.
12. Author’s note: This designation change did not conform to the Tri-Service Designation System impressed on all branches of the U.S. Military and Naval Forces only the year before. The designation A-37 closely identifies the new attack aircraft with its trainer forebear, the T-37. The aircraft should have been designated with the next available number in the attack category, which would have been A-9. THE END
|
Click image below for photo album |
 |
 |
| HOME |
| EMAIL WEBLACKEY |
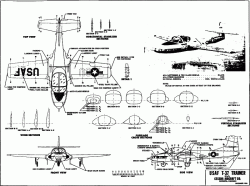 The small jet power plants, of French origin, would be built in the USA by Continental as the J69. The XT-37 prototype 54-0716 made its first flight in the hands of Bob Hogan from the Wichita, KS., Municipal Airport on 12 October 1954.
The small jet power plants, of French origin, would be built in the USA by Continental as the J69. The XT-37 prototype 54-0716 made its first flight in the hands of Bob Hogan from the Wichita, KS., Municipal Airport on 12 October 1954. Other observers who took note of the aircraft’s audible output
dubbed it the Air Force’s best kerosene-to-decibel converter. The first production batch of eleven aircraft (54-2729/54-2739) is referred to as an evaluation batch by some sources.
Other observers who took note of the aircraft’s audible output
dubbed it the Air Force’s best kerosene-to-decibel converter. The first production batch of eleven aircraft (54-2729/54-2739) is referred to as an evaluation batch by some sources. A total of 1,237 Cessna jet trainers had been delivered by 1 January 1972, with all T-37As converted to T-37B standard.
A total of 1,237 Cessna jet trainers had been delivered by 1 January 1972, with all T-37As converted to T-37B standard.
 T-34A
Mentor began to replace the remaining T-6Gs at the Air Force primary training
schools. Following 30 hours of instruction in the T-34A, students would then
progress to the T-28A. Beginning with the service introduction of the T-37A in
1957, students progressed from the T-34A to the new Cessna jet. The T-34A
primary training phase was dropped in April, 1961 when the Air Force introduced
an all-jet training syllabus. Within a short period, the expense of this plan
became evident when examining the cost of student drop-out. In July, 1964, the
Cessna T-41A Mescalero, essentially an “off-the-shelf” Cessna Model 172, was
selected to become the Air Force’s new piston basic trainer. Following a
successful 30 hour primary phase in the economical Cessna prop trainer, students
would then progress to a 90 hour phase on the T-37.
T-34A
Mentor began to replace the remaining T-6Gs at the Air Force primary training
schools. Following 30 hours of instruction in the T-34A, students would then
progress to the T-28A. Beginning with the service introduction of the T-37A in
1957, students progressed from the T-34A to the new Cessna jet. The T-34A
primary training phase was dropped in April, 1961 when the Air Force introduced
an all-jet training syllabus. Within a short period, the expense of this plan
became evident when examining the cost of student drop-out. In July, 1964, the
Cessna T-41A Mescalero, essentially an “off-the-shelf” Cessna Model 172, was
selected to become the Air Force’s new piston basic trainer. Following a
successful 30 hour primary phase in the economical Cessna prop trainer, students
would then progress to a 90 hour phase on the T-37. The T-41/T-37 platform
combination proved to be what the Air Force needed, and went on to provide over
three decades of pilot training service. The final Air Force student sortie in a
T-37B took place on 17 June 2009.
The T-41/T-37 platform
combination proved to be what the Air Force needed, and went on to provide over
three decades of pilot training service. The final Air Force student sortie in a
T-37B took place on 17 June 2009.